Yesterday I decided to install WordPress for my new blog, both because it seemed like good product for the job and also to get some experience in running it (and thus also PHP) on Windows Server 2012 with IIS 8 Hosting. There are some good resources scattered around the web, but none seemed up to date, so I decided to share my notes from the install on here. I’m assuming you already have Windows Server 2012 and SQL Server 2012 installed.
IIS 8 CONFIGURATION
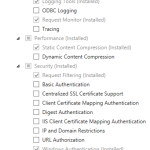
The configuration of IIS 8 is quite easy: you just enable the Web Server role through Server Manager. Just to be complete, the screenshot below shows the options I currently have installed, but keep in mind that I’m also running ASP.NET on my server.
Yesterday I decided to install WordPress for my new blog, both because it seemed like good product for the job and also to get some experience in running it (and thus also PHP) on Windows Server 2012 with IIS 8. There are some good resources scattered around the web, but none seemed up to date, so I decided to share my notes from the install on here. I’m assuming you already have Windows Server 2012 and SQL Server 2012 installed.
IIS 8 CONFIGURATION
The configuration of IIS 8 is quite easy: you just enable the Web Server role through Server Manager. Just to be complete, the screenshot below shows the options I currently have installed, but keep in mind that I’m also running ASP.NET on my server.I also highly recommend you install PHP Manager (http://phpmanager.codeplex.com/) as it will help us in enabling/disabling PHP extensions from within IIS Manager later on and provides an easy way to access php.ini as well.
PREREQUISITE INSTALLATION
To make things easy, you can install and configure PHP quite easily using the Microsoft Web Platform Installer. When you run the Web Platform Installer (Web PI), you can do a quick search for “sql php” and it comes up a few results. When you select “Microsoft Drivers 3.0 for PHP v5.4 for SQL Server in IIS”, which is what we need, all other prerequisites will be automatically installed as well as dependencies (PHP and URL Rewrite for IIS).
After Web PI finishes, you will have PHP installed and configured for use in IIS. Time to do a little test to see if everything is running smoothly. Create a new file under C:\inetpub\wwwroot\ (or wherever your Default Web Site is pointing to) named test.php with the following content:
<?php echo phpinfo(); ?>
This will output information about your PHP configuration.
Time to try it out: navigate to the page (likely http://localhost/test.php). If you are greeted with a screen with purple blocks of information about your PHP configuration, you’re all set and you can skip ahead to the WORDPRESS INSTALLATION section. Chances are you’re going to be greeted with an IIS 403.1 error screen, however, which is due to the fact that the user account that IIS is currently using for the anonymous access to your site doesn’t have the proper privileges to access your wwwroot (or equivalent) folder on disk. This is solved quite easily by granting this user (called IUSR by default) access to the wwwroot folder through Windows Explorer or your other favorite method.
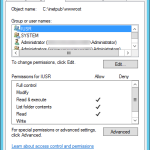
Retry and bask in the glory of the phpinfo() output.
WORDPRESS INSTALLATION
Now we can start downloading the actual WordPress files and start the installation. First off, grab the latest version (or the version of your choice) of WordPress. We will also need the WP Db Abstraction plugin. After downloading, unblock and unZIP both files in a folder under wwwroot (or your Web Site’s location). Installation of the WP Db Abstraction plugin is quite easy, just follow the steps outlined in the readme.txt:Upload wp-db-abstraction.php and the wp-db-abstraction directory to wp-content/mu-plugins. This should be parallel to your regular plugins directory. If the mu-plugins directory does not exist, you must create it.
Put the db.php file from inside the wp-db-abstraction.php directory to wp-content/db.php
Visit $your_wordpress_url/wp-content/mu-plugins/wp-db-abstraction/setup-config.php to generate your wp-config.php file
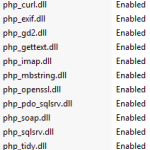
Before you perform the last step, though, go to IIS Manager and enter PHP Manager (it’s located on the Features page of your server under IIS). Scroll down and click the “Enable or disable an extension” link. You need to make sure that php_pdo_sqlsrv.dll and php_sqlsrv.dll are both enabled. You can also go ahead and disable the *mysql*.dll extensions. Here’s my list of enabled extensions:
Now we can visit the setup-config.php page as outlined above. The steps here are quite straightforward, so I’m not going to walk you through them. You will need to create a user on your SQL Server 2012 installation with SQL Server authentication that has access to a database that you also need to create to use for your WordPress installation.
One note about this process: I had some issues when choosing the default selected “SQL Server using MS PHP driver” and went with the “PDO SqlSrv” option the second time to eliminate these issues.
If the wizard has trouble automatically creating the wp-config.php file, you can either choose to give IUSR write permissions on the folder you created to hold all your WordPress files or you can manually create the file under that folder and paste the output you see on screen in there (I chose the latter). After the wp-config.php file is created, you can start the installation of WordPress by clicking the link on the bottom of the page you’re on.
WORDPRESS CONFIGURATION
After the install, which should only take a minute tops, you are now ready to log in to your WordPress admin dashboard and start configuring it how you’d like. As you can see, there’s a sample post and comment already waiting for you. If your experience is anything like mine, you will notice that when you navigate to the Posts -> All Posts option on the top left of your dashboard you won’t actually see these posts in the list. It took some hunting around the web to figure this out, but apparently there’s a line in the translations.php file of the WP Db Abstraction plugin that’s causing this (thanks to tm3ister on http://sourceforge.net/projects/wp-sqlsrv/forums/forum/1124403/topic/5004241 for figuring this out!). The solution is to manually edit the translate_limit function in the mu-plugins/wp-db-abstraction/translations/sqlsrv/translations.php file:
Change
// Check for true offset
if ( (count($limit_matches) == 5 ) && $limit_matches[1] != '0' ) {
$true_offset = true;
} elseif ( (count($limit_matches) == 5 ) && $limit_matches[1] == '0' ) {
$limit_matches[1] = $limit_matches[4];
}
To
// Check for true offset
if ( (count($limit_matches) == 5 ) && $limit_matches[1] != '0' ) {
$true_offset = true;
} elseif ( (count($limit_matches) >= 5 ) && $limit_matches[1] == '0' ) {
$limit_matches[1] = $limit_matches[4];
}
And voila, your posts will now show up.
The last thing we’re going to configure is Permalinks (or pretty URLs) for our posts. When you navigate to Settings -> Permalinks on the admin dashboard, you’ll see some options to rewrite URLs to be more human and search engine friendly. For now, select Custom Structure and enter /%year%/%monthnum%/%postname%/ in the text field and hit Save Changes. The last step is to create a web.config file in our WordPress folder to rewrite the URLs according to this scheme with IIS URL Rewrite. Create a new web.config file (if you don’t have one already) in the folder you installed WordPress to and copy in the following:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<configuration>
<system.webServer>
<rewrite>
<rules>
<rule name="wordpress" patternSyntax="Wildcard">
<match url="*" />
<conditions>
<add input="{REQUEST_FILENAME}" matchType="IsFile" negate="true" />
<add input="{REQUEST_FILENAME}" matchType="IsDirectory" negate="true" />
</conditions>
<action type="Rewrite" url="index.php"/>
</rule>
</rules>
</rewrite>
</system.webServer>
</configuration>
You’re now all set to use WordPress on Windows Server 2012 with IIS 8 and SQL Server 2012!