To make any application accessible to the end-user, we need to host it on a server. So, in this article, we will learn how to host ASP.NET Web API REST Service in IIS 10. The following steps are required to host any application.
Step 1 Install IIS
Before hosting any application, make sure that IIS (Internet Information Services) is installed on your Hosting Server. If it is not installed or enabled, then follow the below steps.
Click on Windows icon at the bottom left corner and find the "Control Panel" menu and click on it.
In the "Control Panel", find the "Program and Features" option from the displayed list.
This shows the list of installed programs. Find and click the "Turn Windows feature on or off" option from the left pane, as shown in the following image.
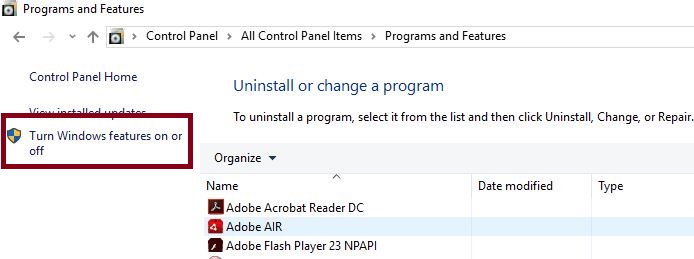
Now, in the next popup, find Internet Information Services (IIS) and check on it.
Click "Next" button and then "Finish". It takes a few minutes to install IIS.
After installing IIS, restart your machine.
Note - I have Windows 10 OS and the above process is for Windows 10 PC. The steps might differ depending on your Operating System version.
Step 2 Install .NET Framework
Although Visual Studio is not required on your hosting Server, it must have .NET Framework installed, as per the .NET framework used to develop the application. If it is not installed, then please install the appropriate .NET Framework available on Microsoft official website.
I assume, you have installed the .NET framework on your Hosting Server.
Step 3 Move the published code on Hosting Server
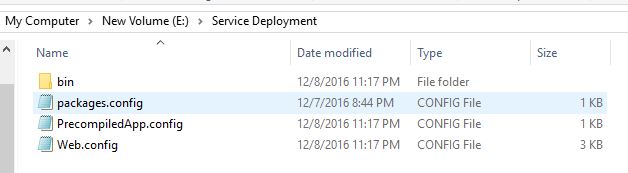
Copy the "Published files" and paste those on respective Servers where you want to host the Web API REST Service. In our last article, we published Web API REST Service in the E drive of my Server, as shown in the following image .
Step 4 Open IIS Manager
Now, open the IIS Manager from Windows menu or in any other ways you have known.
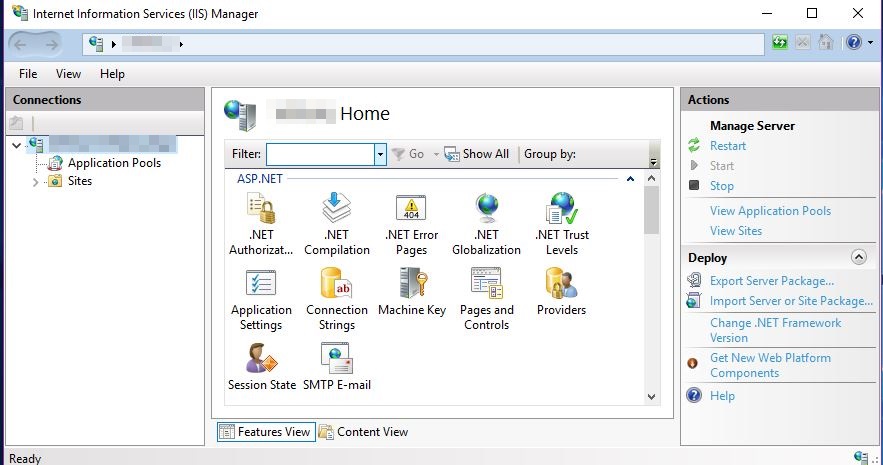
The above image is of IIS 10 Manager of my Windows 10 machine. The view as well as options might be different on your machine depending on the OS version.
Step 5 Add Website
Right click on "Site" in IIS and click on add new website, as shown in the following screenshot.
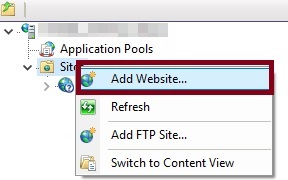
After clicking on "Add Website" option, it displays the following configuration window.
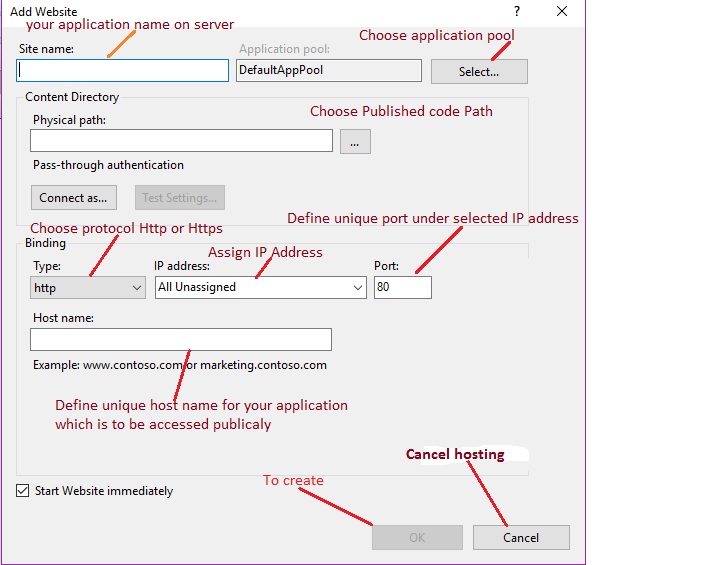
I hope you understood the preceding configuration by highlighted text.
Step 6 Define Site Name & Application Pool
Define the site name which will be useful to uniquely identify the site within the IIS Server. After specifying the site name, choose the Application Pool from available pools. You can even create a custom application pool with any desired name. Currently, our IIS Manager has the following Application Pools.
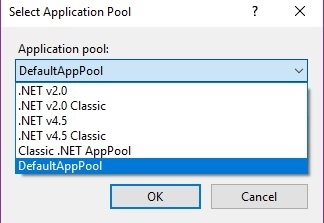
Choose the application pool depending on your application configuration. In this article, we are going to choose DefaultAppPool.
Step 7 Browse and select Published Folder path
Now, choose the physical location of published code files by clicking on "Browse" button, as shown in the following image.
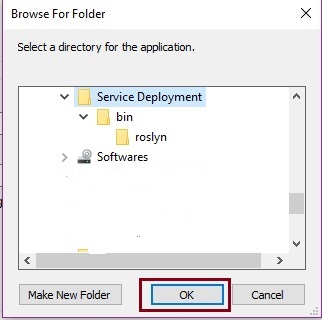
Now, click on "OK" button.
Step 8 Define IP address & Port
Choose one IP address from the list of available IP addresses and define the unique port number for the application, which will be unique within the defined IP address.
Step 9 Choose Protocol & Host name (optional )
Choose the protocol for your application i.e HTTP or HTTPS which requires port 443 to be open and choose the Host name which will be used publicly to access the application. After defining all the configurations, the web site configuration window will look like this.
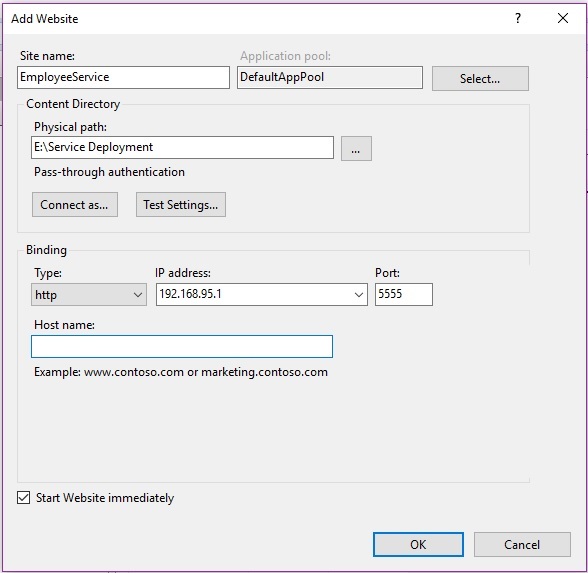
Now, click on OK button. It will create and add the application in IIS.
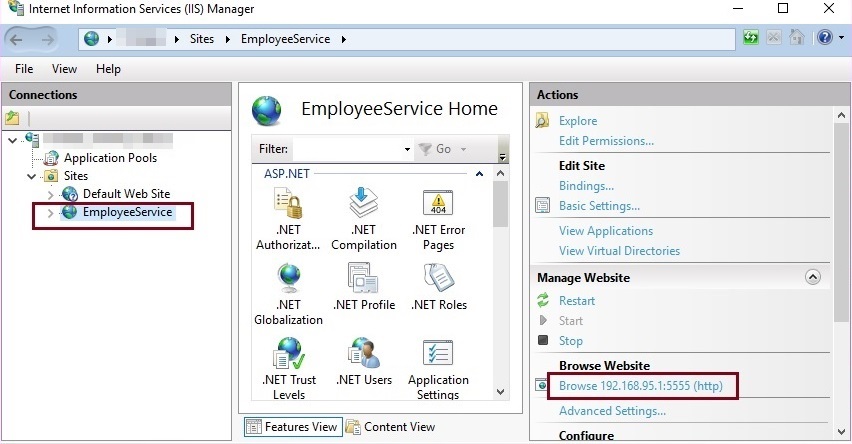
Step 10 Browse the URL with REST Client
Browse the hosted application using REST client with base URL along with API, Controller name, and Action method name, with pattern defined in routing template inside the webapiconfig.cs file.
We can browse applications using the browser but then, we can only test the GET method. So, to test all types of Action Methods, we are using advanced REST client which is a developer extension tool in Firefox browser.
Our hosted Web API REST Service includes these two methods, as given below.
GetAllEmployees (GET )
GetEmployeeById (POST ) which takes id as input parameter
Browse GetAllEmployees method using Advanced REST client which has used HTTP GET verb.
The GetAllEmployees hosted Web API REST method is returning all the employee lists.
Now, browse GetEmployeeById method using Advanced REST client which uses HTTP POST verb and takes id as input parameter.
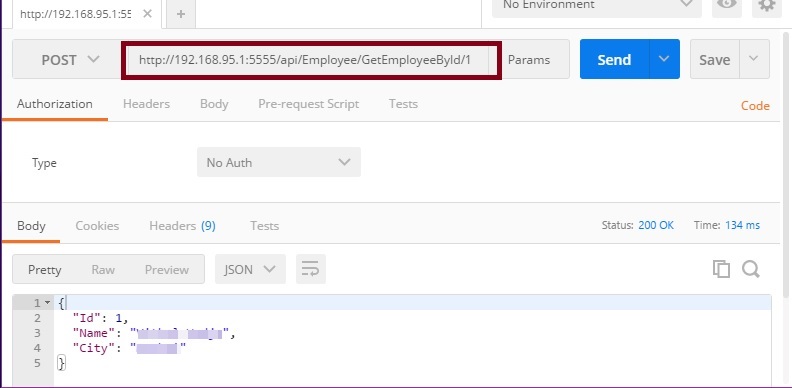
From the above desired output, it's clear that our Web API REST Service is hosted on IIS successfully.
Note
Download the Zip file of the Published code to learn and start quickly.
This article is just guideline to show how to host Web API REST Service on IIS .
Optimize the speed by setting debug as false etc., from web.config file as per your skills.
In this article, the optimization is not covered in depth.
Configure the authentication in IIS as per your REST Service .
Summary
I hope, this article is useful for all readers. If you have any suggestions, please mention them in the comments section.