
November 22, 2024 07:01 by
 Peter
PeterInstall the latest .NET Core SDK - not sure if .NET 8 is enough for old ASP.NET. Any way install both .NET 8 and .NET standard framework (.net 4.8.1). Install the latest .NET Core runtime(I guess .NET 8 installation takes care of it, anyway. If things dont work - install .NET runtime separately)
This software is important - I guess it is ASP.NET Core runtime.
Anyway, google --- ASP.NET Core runtime - Windows Hosting Bundle Installer -- whatever software suggestion comes in Google, pls install it.
Whenever you migrate to the latest version, Install the above software in Windows Server 2022
Of course, we need to install the latest IIS on the Windows server.
I will write a separate article about the IIS Migration
For IIS migration, list all software present in the old server. Install all this software on the new server. If you miss any software, there will be a code break/your apps will not work on the new server.
If you are using Excel Libraries on the old server, this may not be allowed on the new server. Use NPOI/EXcelDataReader opensource nugest package instead.
Below are the steps for IIS 10 Migration
First, we have to export all IIS settings from IIS 6 or IIS 8.
The settings will be exported/saved as a zip file.

You may get an error, or export settings may fail if you try to export all IIS settings.
So we have to export one set by one. Please follow the below steps.
In IIS 8/IIS 6/Old Server.
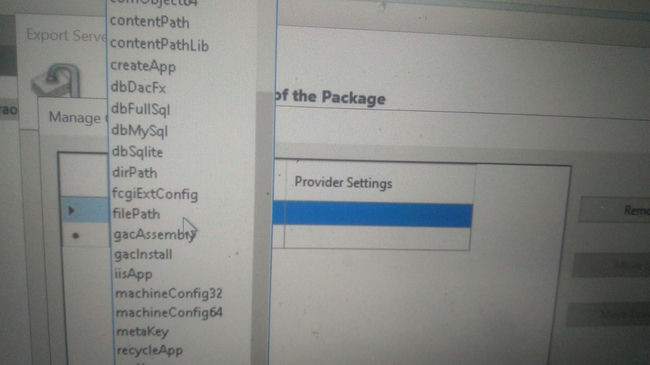
Right-click IIS => Export Server Package => Manage Components.
We have to export each item using the provider name dropdown.
Webserver and webserver60 are important.
Before exporting, delete unwanted files inside a physical directory because exporting some of the items in the dropdown may fail if the physical directory size is large.
After exporting, import each component's settings.
Right-click IIS => Import and import zip file settings in the same order they are exported.
Importing some components may fail, but move on to the next component.
Dont stop if you get errors while importing or exporting some of the components. Yes, you may not be able to export some of the settings, but dont worry. Move on to the next setting.
When you install IIS from Server Explorer, Imort Option may not be there when you right-click IIS.

November 18, 2024 08:15 by
 Peter
PeterInstalling and activating IIS Express on Windows (11/10) is described in this article. Start by downloading IIS Express from the Microsoft website's official IIS Express page. After that, install the software by opening the installer and following the prompts on the screen. Verify from the Start menu after installation.

To activate IIS Express, take the actions listed below.
Step 1. Search and open "Turn Windows features on or off" from Control Panel > Programs and Features
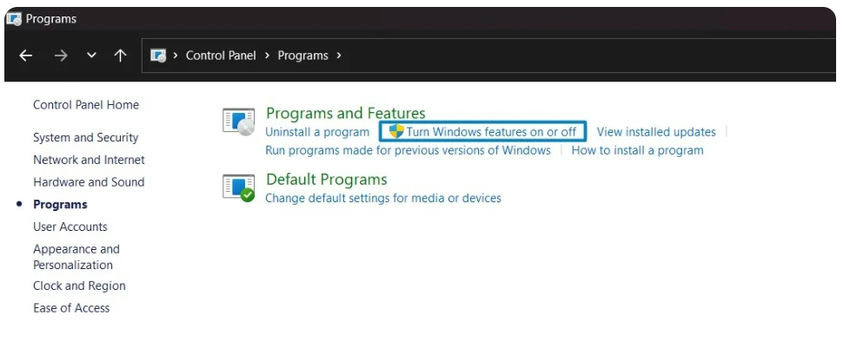
Step 2. From "Turn Windows features on or off" window search and on check box "install and enable the IIS express" option and click ok.
Step 3. Windows Feature update will update the required files. After Completing Click Close.
After completion go to start menu and search IIS Express manager will get enable in your system.

October 10, 2024 09:08 by
 Peter
PeterImagine this: A critical Windows service that you just launched is meant to maintain the seamless operation of your organization. However, the moment you launch it, the service abruptly ends after 30 seconds, leaving you furious and scratching your head. Users are experiencing problems that are becoming worse by the minute, and the logs aren't offering definitive explanations. What isn't working well?
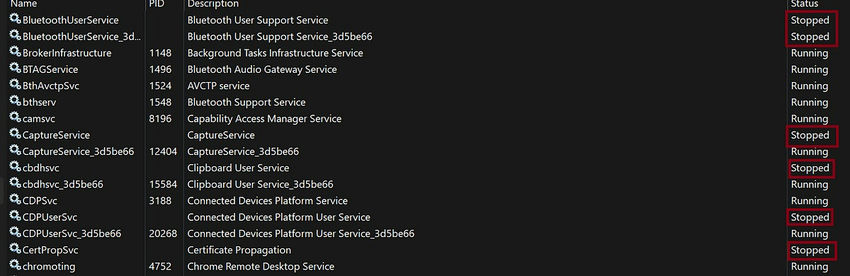
Stopped services
This is a scenario that many developers and IT professionals encounter when working with Windows services. The core of this problem is a specific behavior enforced by the Service Control Manager (SCM), which expects the OnStart method of your service to complete within a strict 30-second window. If your service doesn’t comply, the SCM will assume a failure and halt the service.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into the reasons why your Windows service might be stopping right after it starts and explore the mechanics behind the SCM’s behavior. Whether you’re troubleshooting an existing service or designing a new one, understanding this common factor will help you create more resilient and reliable services.
To resolve this issue, consider the following approaches.
- Optimize Initialization Code: Review and refactor the code in the OnStart method to ensure it executes as quickly as possible. If certain operations are time-consuming, consider moving them to a separate thread or background worker. Make sure executing the Onstart method does not take more than 30 seconds.
- Increase the Timeout: This approach is not recommended as a first step. It’s possible to extend the startup timeout by modifying the service’s properties in the registry. However, this should be done with caution, as it may lead to other performance issues.

Follow the below steps to increase service time out.
- Press Win + R, type regedit, and press Enter. This opens the Windows Registry Editor.
- In the Registry Editor, navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control.
- Right-click on the Control key, select New, then DWORD (32-bit) Value.
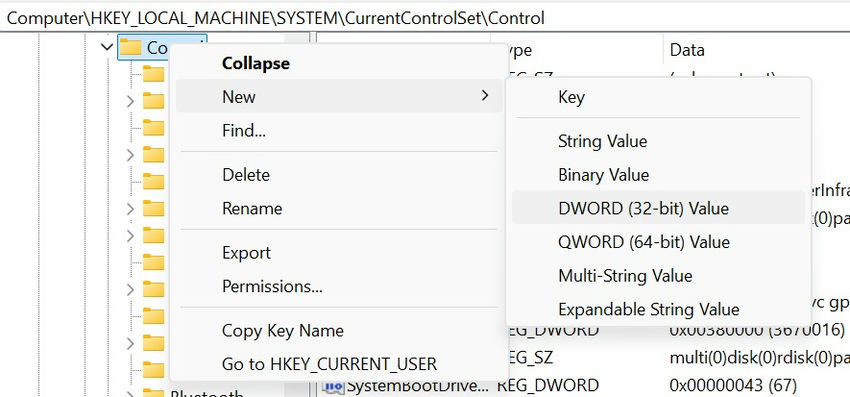
Regedit
- Name this new value “ServicesPipeTimeout”.
- Double-click the “ServicesPipeTimeout” value you just created.
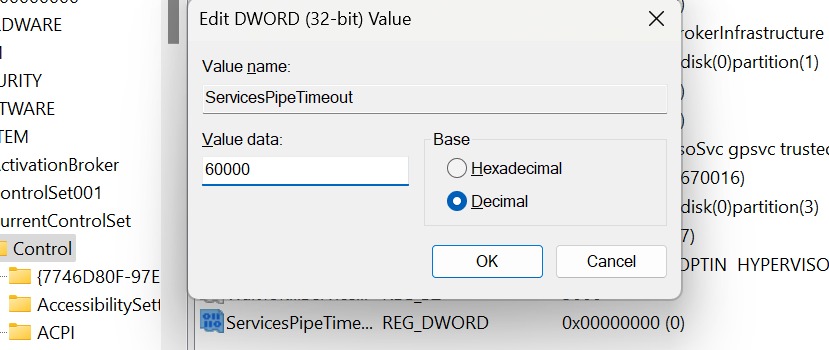
ServicesPipeTimeout
- In the “Value data” field, enter the desired timeout value in milliseconds. In this case, we will be setting a timeout of 60 seconds, so we will input “60000” as value data and ensure that the base is set to Decimal.
- For the changes to take effect, restart your system.
Important note
- Modifying the registry can have unintended side effects if not done correctly. Always back up the registry before making any changes.
- The “ServicesPipeTimeout” value affects all services on the system, not just the specific service you're troubleshooting.
- While increasing the timeout can prevent premature service stoppages, it can also delay the detection of legitimate service startup failures.
Conclusion
While increasing the timeout via the registry is an option, it’s often more recommended and also effective to optimize your OnStart method or use asynchronous tasks. By doing so, you can prevent premature service stoppages and ensure your service runs smoothly and efficiently.

August 23, 2024 07:47 by
 Peter
PeterWe can parse various log kinds with the aid of Log Parser Studio. The primary topic of this lesson will be IIS log parsing. There are two Log Parser programs: one that can only be used with a command prompt and the other that includes full GUI support.

Installation
Below is the sample query for Log Parser with GUI to get the output from IIS logs for a URL and other data like [MAX, MIN, AVG] – Response Time in mili seconds and hits.
SELECT cs-uri-stem as URL,
MAX(time-taken) As Max,
MIN(time-taken) As Min,
Avg(time-taken) As Average,
Count(1) as Hits
FROM '[LOGFILEPATH]'
GROUP BY URL
ORDER BY Average DESC
Below is the sample query to run in Log Parser with the command prompt version.
Logparser -i: iisw3c “ SELECT cs-uri-stem as URL,
MAX(time-taken) As Max,
MIN(time-taken) As Min,
Avg(time-taken) As Average,
Count(1) as Hits from D:\test.log GROUP By URL ORDER BY Average DESC TO D:\result.csv” –o : csv
Usage details Log parser studio
The landing screen of Log Parser Studio is given below.
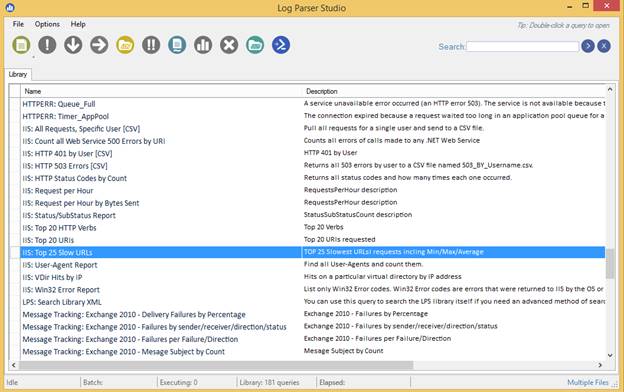
As we are interested in parsing IIS logs, so select IIS-Top25 slow URLs.
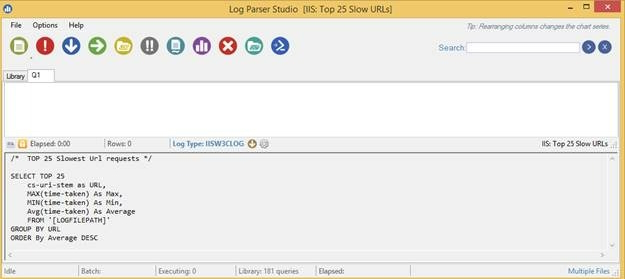
The query with all the details will be shown to the user.
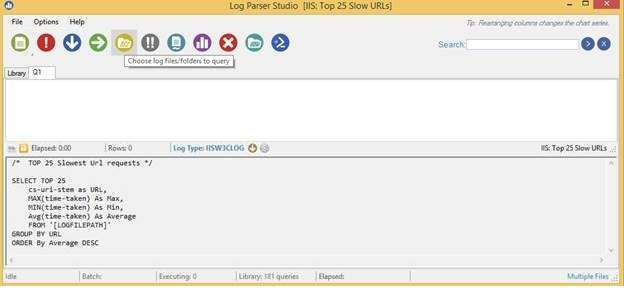
Now, we need to choose the IIS logs file. Click the Choose log files icon.
The dialog box with the options will be shown, where we have to select the individual log files or the folder. Now, we need to click the icon to execute an active query.
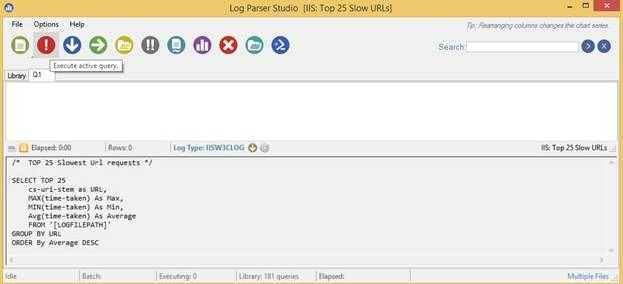
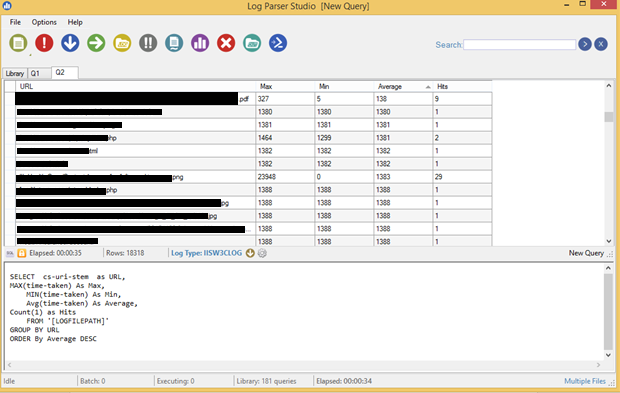
Below is the screenshot of Log Parser Studio with the results. The data for Max, Min, and Average refers to Response Time in mili seconds. We can copy data or export the data, as required.

July 10, 2024 08:24 by
 Peter
PeterI'm using Windows 10 Enterprise Edition in my instance. Now launch the browser and enter http://localhost/ as the URL.
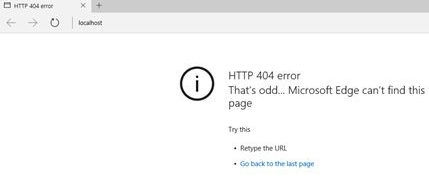
A page not found error will appear when you press Enter.
I'm going to look for the IIS manager now.

Not located!
Slide the Control Panel open.
Click Programs.
Under Programs and Features, click Turn Windows features on or off.

A new popup will appear.
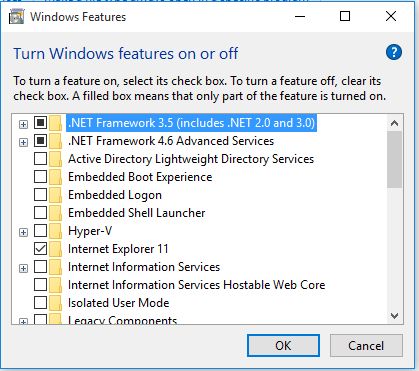
Just check the Internet Information Services and its related features. Under Internet Information Services check the following folders.
- FTP Server
- Web Management Tools
- World Wide Web services
- Application development features
- Common HTTP Feature
- Health and Diagnostics
- Performance Feature
- Security
Then click OK to complete the installation of new features.

Click Restart now to apply changes to complete the IIS feature installation.
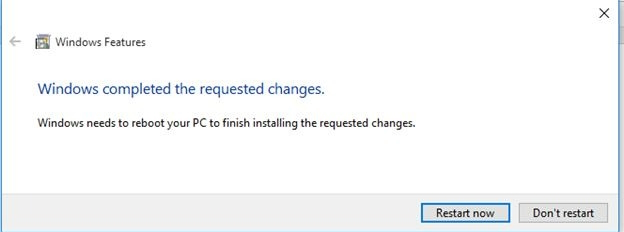
After a successful restart.
Now you can see the IIS webserver option on the All Programs menu.
Open the browser.
Now type URL http://localhost.
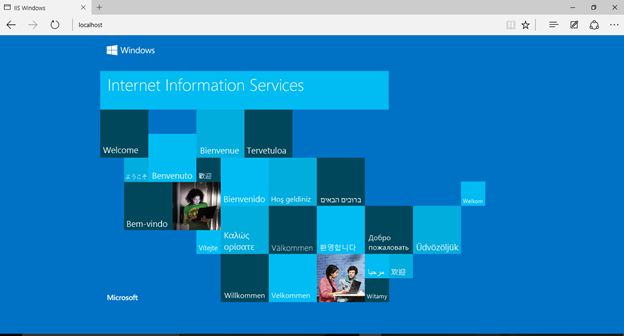
Internet Information Services (IIS) successfully configured.
Summary
In this article, we learned about Configure IIS In the Windows 10 Operating System.

January 17, 2024 07:01 by
 Peter
PeterHave you ever seen a blank screen or 404 error when trying to reload a page in a React Router-powered application? This happens when there are no defined routes in the application's routing setup that match the URL path.

Note: I've been having trouble with this and have since figured out a solution, so this is only for Windows server hosting.
This is happening as a result of the Single Page Application (SPA) that your website is built on React. Your application, index.html, loads automatically when you access the website through the root directory. and hence you never truly leave the index.html page even when you navigate to other pages.
Make sure the URL Rewrite module is enabled in your server setup. You can change or rewrite the URLs with this module.
- Go to Control Panel -> Programs -> Programs and Features.
- Click on "Turn Windows features on or off" on the left sidebar.
- Scroll down and locate "Internet Information Services," expand it, and then select "World Wide Web Services" -> "Common HTTP Features" -> "URL Rewrite."
- Click "OK" and let the feature be installed.
Once the URL Rewrite module is enabled, open your project's web.config file (located in the root directory of your application).
<system.webserver>
<rewrite>
<rules>
<rule name="React Router" stopProcessing="true">
<match url=".*" />
<conditions logicalGrouping="MatchAll">
<add input="{REQUEST_FILENAME}" matchType="IsFile" negate="true" />
<add input="{REQUEST_FILENAME}" matchType="IsDirectory" negate="true" />
</conditions>
<action type="Rewrite" url="/" />
</rule>
</rules>
</rewrite>
</system.webserver>
Note: Before using the aforementioned technique, make sure your React application is developed and deployed correctly on the Windows server.