The log files that IIS generates can, over time, consume a large amount of disk space. This article will discuss a way to remove the IIS Log Files, including locate the log file directory. The content of this article is

Introduction
- Problem
- How to locate the IIS Log File Folder
- Run the VB Scrip
Problem:
IIS log files continue to grow in Web Server and can, over time, consume a large amount of disk space. Logs can potentially fill up an entire hard drive. To mitigate this problem, many users turn off logging completely. Fortunately, there are alternatives to doing so, such as the following:
- Enable folder compression
- Move the log folder to a remote system
- Delete old log files by script.
Here we will discuss the third option.
How to locate the IIS Log File Folder
By default, the IIS log file folder is in %SystemDrive%\inetpub\logs\LogFiles, it is usually in C:\inetpub\logs\LogFiles. However, the location can be customized by user. We have two ways to locate the IIS Log Folder
- through IIS Manager
- through Running a Script, such as Windows PowerShell Script
Through IIS Manager:
Open IIS Manager => Click the Chosen Site under Sites => Double Click the Logging Icon
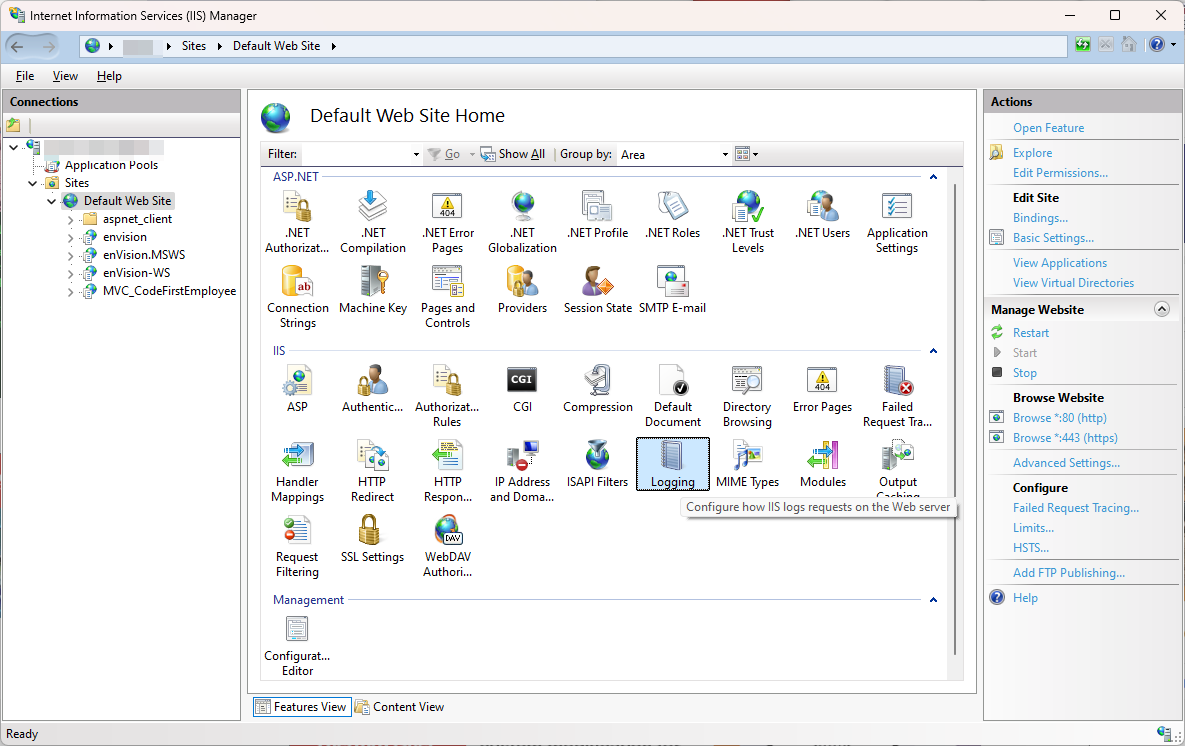
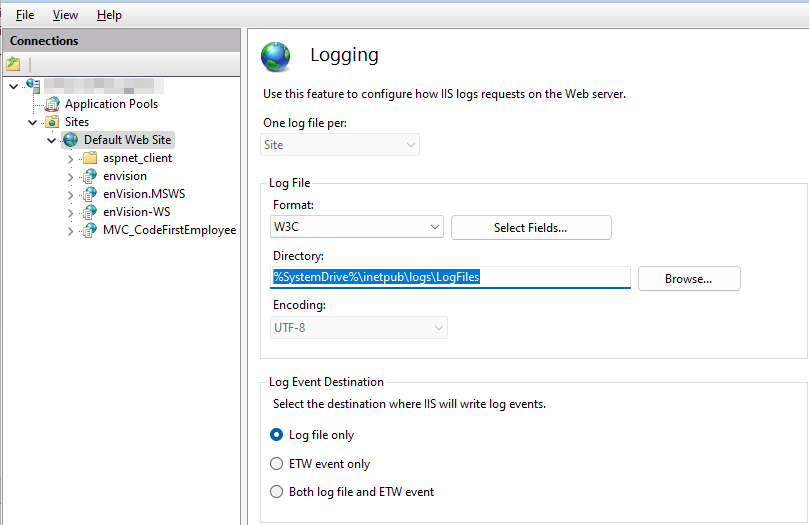
In the Logging page, the IIS Log File Folder is shown in the Direcitory:
such as %SystemDrive%\inetpub\logs\LogFiles by default
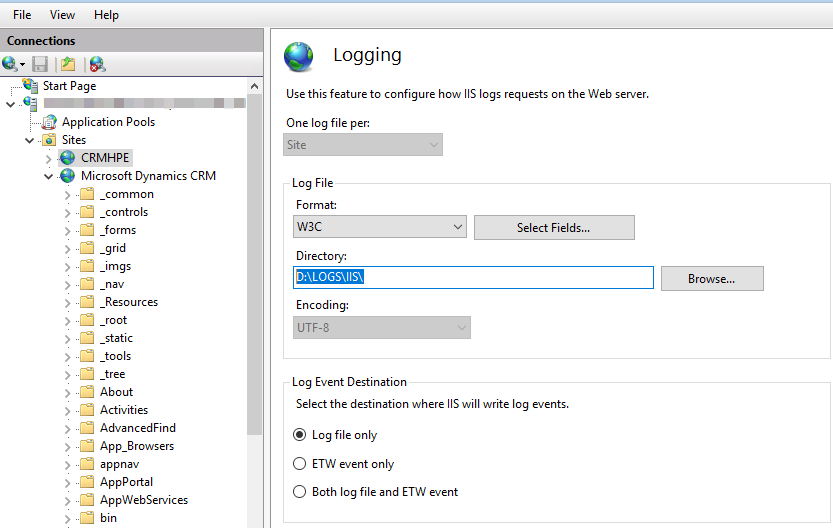
In certain case, it is set by user,
such as D:\LOGS\IIS\
Through Windows PowerShell Script:
Import-Module WebAdministration
# Replace 'Default Web Site' with the name of your website
$siteName = 'Default Web Site'
# Get the log file directory
$logFilePath = Get-ItemProperty "IIS:\Sites\$siteName" -Name logFile | Select-Object -ExpandProperty Directory
Write-Output "The log files for '$siteName' are located at: $logFilePath"
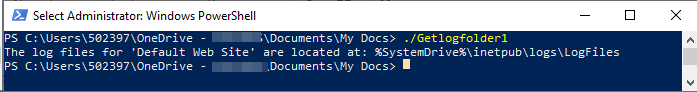
If we put the code in a PowerShell Script file: GotLogFolder1.ps1, we got the default folder:
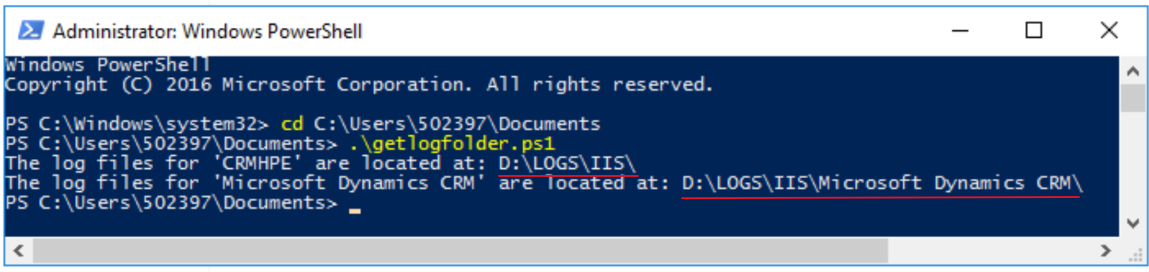
In a customized case, the folder could be different:
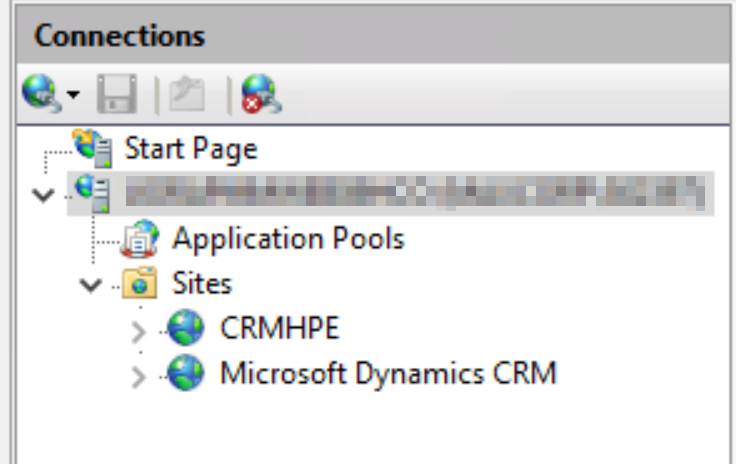
For the IIS structure:
Run VB Script to Remove the IIS log files by Retention Policy
Microsoft provide a VB Script to implement this:
You can control disk usage of log files by running a script that automatically deletes log files that are older than a certain age. Running this script in a scheduled task will keep the problem of a disk filling up under control without constant maintenance.
The following VBScript will check the age of each log file in a folder and will delete any log file older than a specified age. To customize the script for your purposes, simply change the name and path of the folder in line 1 of the script, and change the maximum age to the desired value in days, in line 2.
sLogFolder = "c:\inetpub\logs\LogFiles"
iMaxAge = 30 'in days
Set objFSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
set colFolder = objFSO.GetFolder(sLogFolder)
For Each colSubfolder in colFolder.SubFolders
Set objFolder = objFSO.GetFolder(colSubfolder.Path)
Set colFiles = objFolder.Files
For Each objFile in colFiles
iFileAge = now-objFile.DateCreated
if iFileAge > (iMaxAge+1) then
objFSO.deletefile objFile, True
end if
Next
Next
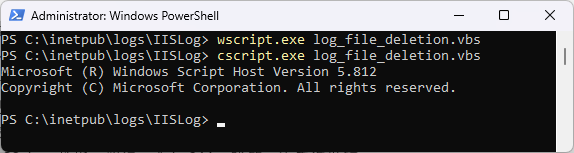
How to run the VB Script?
Windows Script Host enables you to run scripts from Windows ether by WScript or CScript, you still run the scripts in the same manner. The difference is only in the output — WScript generates windowed output, while CScript sends its output to the command window in which it was started.